Step 6. Collect Information About the Current R Session.
Contact Us
The Centre for Artificial Intelligence Driven Drug Discovery (AIDD) at Macao Polytechnic University
Two Sample Mendelian Randomization
A powerful method to estimate causal effects of exposures on outcomes using genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics
The TwoSampleMR package combines three important components to make causal inference accessible and reliable.
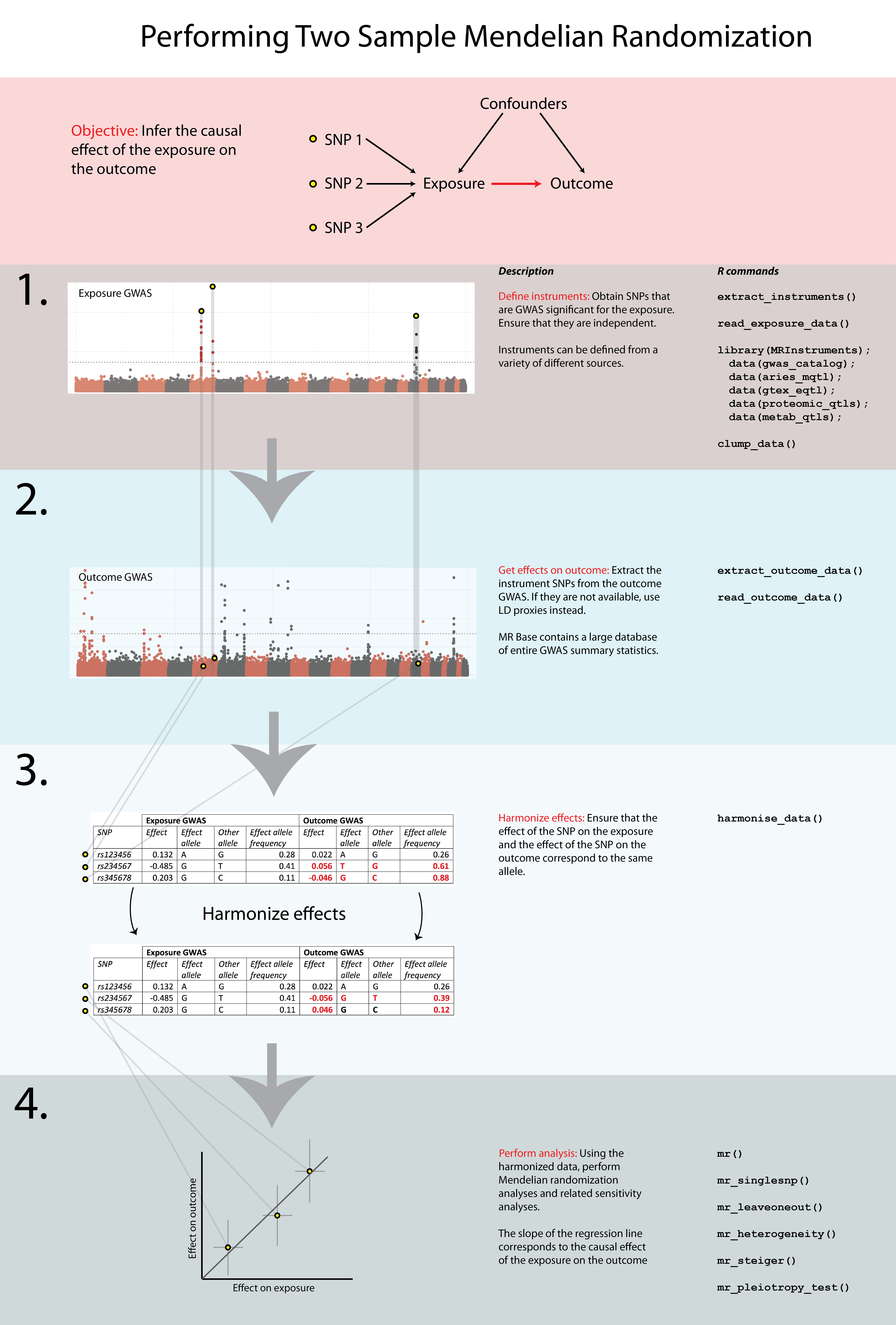
Analysis Workflow
The general principles and statistical methods can be found elsewhere. Here we outline how to use the application based on the TwoSampleMR R package.
Workflow Overview
Critical Considerations
Essential guidelines for responsible and effective Mendelian randomization analysis
Methodological Rigor
While democratizing MR methodology is crucial, atheoretical applications pose significant risks. Avoid randomly selecting exposure-outcome pairs without biological justification or established hypotheses.
Best Practice: Ground analyses in well-defined, evidence-based hypotheses and adhere to established guidelines [1]. Consider biological plausibility, pleiotropic pathways, and implement comprehensive quality control including F-statistics evaluation and heterogeneity assessment.
1. Guidelines for performing Mendelian randomization investigations: update for summer 2023
Evidence Integration
MR results should never be interpreted in isolation. Robust causal inference requires integrating multiple analytical strategies and evidence sources.
Recommended Approach: Combine univariable MR (basic causal relationships), multivariable MR (controlling confounders), and mediation MR (causal pathways) with complementary analyses including colocalization, fine-mapping, and experimental validation. Treat MR as contributory evidence, not definitive proof.
Known Limitations
Methodological constraints require careful consideration during interpretation. Key limitations include population stratification differences, shared genetic architecture assumptions, and horizontal pleiotropy vulnerability.
Critical Issues: Sample overlap bias, differential LD patterns across populations, weak instrument bias, inability to model time-varying effects or non-linear relationships, and challenges in detecting pleiotropic effects using summary statistics. Statistical power depends on instrument strength and GWAS sample dimensions.